In this article:
Eggs, often referred to as “nature’s multivitamin,” are indeed a powerhouse of nutrition.
Let’s delve into their remarkable qualities:
Eggs are rich in High-Quality Protein
- Protein Content: Eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein. A single large egg contains approximately 6 grams of protein. This protein is considered complete, meaning it provides all the essential amino acids our bodies need for various functions.
- Biological Value: The biological value of egg protein is exceptionally high, which indicates how efficiently our bodies can utilize it. Eggs score close to 100% on this scale, making them an ideal protein source for muscle repair, immune function, and overall health.
Eggs are a great source of Choline
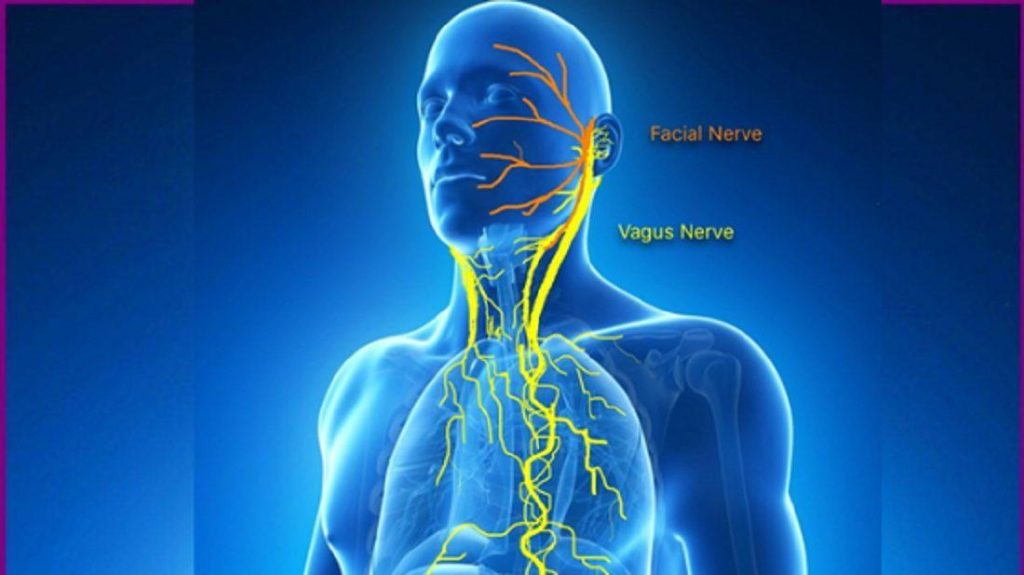
- What Is Choline?
Choline is a vitamin-like compound that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is essential for brain health, cell membrane structure, and neurotransmitter synthesis. - Cognitive Benefits:
Regular consumption of choline-rich eggs has been linked to improved cognitive performance and a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline1. - How is choline helpful?
Choline is used to make acetylcholine, the most abundant neurotransmitter in the body. Choline is absolutely essential for many functions of the vagus nerve, which is the main contributor in the body for your ability to rest, recover, and fight stress. - Choline Content:
A single egg provides approximately 147 mg of choline, with almost all of it concentrated in the yolk.
Cholesterol and Heart Health… do you really need to worry
- Eggs have been criticized due to their cholesterol content. However, dietary cholesterol from eggs has minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels. In fact, in 70% of people, eating cholesterol may not raise blood cholesterol or only mildly raise it. The liver produces cholesterol daily, adjusting its production based on dietary intake. When you have more cholesterol you need in your blood, the liver signals to the intestine to absorb less of it, and produces less too. If you want to know more about cholesterol, read my article here.
- Contrary to popular belief, studies show that eggs can improve your cholesterol profile. They raise HDL (good) cholesterol and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol. Nontheless, more research is needed.
- Multiple studies found no association between egg consumption and heart disease risk. In fact, some research suggests health benefits, such as improved insulin resistance and favorable lipid profiles. Some other showed instead a slight increase in heart disease risk. Once again, we need more research before jumping to a conclusion.
Low quality eggs might indeed be bad for you
 The European Union has defined an egg code that consists of
The European Union has defined an egg code that consists of
- a number indicating the method of production (see below)
- a two letter code for the country of origin (in the picture: “DE”)
- a registration number indicating the hen laying establishment (in the picture: “1344461”)
The egg stamp is required in the EU on all class A eggs unless these are sold directly on the farm.
Method of production
The first number of the egg code defines four methods of hens raising:
- 0: organic egg production – BEST
- 1: free-range eggs – BETTER
- 2: deep litter indoor housing – BAD
- 3: cage farming – REALLY BAD
From 0 to 3, the nutrition score of the eggs might drop significantly: free range eggs are much richer in vitamins and healthy fat, and organic eggs should be free from antibiotics. Long-term consumption of food containing antibiotics is a well known cause of many health problems, such as chronic inflammation, IBS, allergies and immuno deficiencies.
In summary, eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, offering protein, choline, and essential nutrients. While concerns about cholesterol exist, most people can enjoy eggs without worry. If you want to know if you are one of these, check my article about the causes of high cholesterol and heart diseases.
Remember: low quality eggs might be lower in healthy fats and vitamins, while they might contain antibiotics. Opt for high-quality eggs, LEVEL 1 AT LEAST, and remember that the majority of nutrients reside in the yolk. 🥚🌟
Disclaimer
Consult a health professional before making significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or supplement regimen. The information provided in this blog is intended to convey the latest scientific research in an accessible manner. However, it does not replace the advice of a medical professional. Take your health conditions into account and consult a qualified healthcare provider to ensure that the decisions you make are safe and appropriate for your specific health needs. Ultimately, you are responsible for your own health and well-being.